Author: Chenglin Pua (Malaysia)
Silicon Valley is the birthplace of many high-tech companies. In Silicon Valley, there is a top incubator that provides a platform for startups to learn and find financing, namely Y Combinator. Since the establishment of Y Combinator, it has incubated many start-up companies, including many blockchain enterprises, such as the famous OpenSea. So among these "alumni", who are the blockchain leaders?
Introduction to Y Combinator
Founded in March 2005, Y Combinator is a venture capital firm that invests in seed-stage startups. Different from traditional venture capital companies, Y Combinator is more like an "incubator" for startup teams and a "training camp" aimed at nurturing startup companies; they not only provide startup companies with a certain amount of seed funding, but also give They offer entrepreneurial advice, as well as three-month “courses” held twice a year to empower entrepreneurial teams to execute. Y Combinator takes an average of 6 percent of the startup's total net asset value in return. During training events, Y Combinator offers a full range of services, starting with a personal one-on-one consultation session with a partner and ending with a Demo Day. However, the partnership doesn't end there, as Y Combinator participants can tap into the alumni network and seek additional funding from the network.
Y Combinator operates in a unique way of investment. Wired, a well-known foreign technology magazine, called Y Combinator "a boot camp for startups"; and company founder Paul Graham was also called "a mentor for a new generation of entrepreneurs" .
As a well-known incubator, Y Combinator has graduated from a group of outstanding blockchain companies. These include the well-known NFT trading market OpenSea, portfolio tracking and accounting software CoinTracker, and Bitcoin smart contract layer Stacks, among others. Almost half of Y Combinator's crypto alumni projects fall into the financial services or infrastructure category, with Web3 and NFTs/gaming a close second.
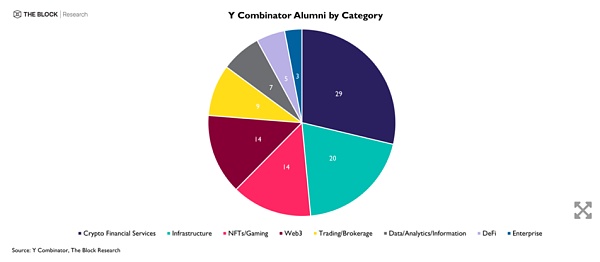
Category Source for Y Combinator Blockchain Alumni : Y Combinator, The Block Research
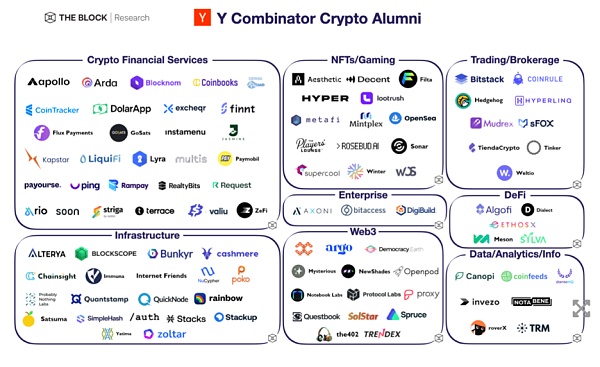
Projects incubated by Y Combinator Source: The Block Research
At present, only OpenSea, Axoni, TRM Labs, and Proxy are the only crypto projects that have received Series B financing among the "alumni" graduating from Y Combinator. More than half of Y Combinator’s “alumni” crypto projects fail to raise follow-on funding after graduation.
In August 2022, Y Combinator sent an email to the founders of the companies it invested in, and put forward several suggestions, so that the founders of the companies could quickly change their minds, plan ahead, and survive this economic recession, which will eventually lead to this economic recession. The ultimate winner of the recession.
Opensea

OpenSea is an online marketplace for NFTs. Opensea was founded by Devin Finzer and Alex Atallah on December 20, 2017 in New York. Users can generate NFTs for free on OpenSea and sell them directly or auction them. OpenSea is primarily based on the Ethereum ERC-721 standard and Polygon (a layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum).
OpenSea received a seed round from Y Combinator in 2018. In November 2019, OpenSea raised $2.1 million in venture capital (primarily from Animoca Brands). In March 2021, OpenSa raised another $23 million in venture capital (mainly from A16z Capital). In July 2021, OpenSea announced another $100 million funding round.
OpenSea had $95 million in revenue in February 2021, $147 million in March, and $2.75 billion in September. In September 2021, OpenSea released its own mobile apps for Android and iOS. In January 2022, OpenSea raised a $300 million funding round (led by Paradigm and Coatue Management) at a valuation of $13.3 billion.
OpenSea co-founder and CEO Devin Finzer said the newly raised funds will be used to improve customer support and security, invest in the wider NFT and web3 community, as well as recruiting and product development. OpenSea is committed to expanding the entire NFT ecosystem. OpenSea will launch a grants program with an opportunity to directly support the developers, builders and creators shaping the future of NFTs. The goal of OpenSea is to facilitate the scale and growth of the wider NFT ecosystem and to invest in the people who shape the NFT space for the better.
Additionally, the funds raised will help OpenSea fend off new competitors in the NFT market. For example, Coinbase is preparing to launch its own NFT marketplace; FTX has an NFT marketplace up and running.
TRM Labs

Founded in 2017, TRM Labs is a blockchain intelligence company that provides risk assessments and helps prevent financial crime and fraud related to the use of digital currencies. TRM Labs tackles data engineering, data science and threat intelligence challenges every day. To date, TRM Labs has raised over $79 million from JPMorgan, Visa, Citi, PayPal, Block, Initialized Capital, Tiger Global, Bessemer and Y Combinator.
Since its launch from Y Combinator incubator in 2019, TRM Labs' revenue has grown by 600% year-on-year, and its team has grown from 4 to 60, and now includes members from the FBI, US Secret Service, and Europol. Security threat finance experts, and data scientists from Apple, Amazon, and Google.
TRM Labs' blockchain intelligence platform visualizes cross-chain data and threat intelligence, on-chain customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, advanced analytics, customer relationship management, etc., and uses big data and machine learning to automatically detect money laundering and market manipulation and other suspicious activities, which in turn helps organizations detect crypto fraud and financial crimes more intuitively and easily, which is why fast-growing cryptocurrency exchange companies such as Circle, FTX US, and MoonPay have chosen TRM Labs to monitor, detect suspicious activities and meet anti-money laundering requirements. reasons for regulatory requirements.
TRM Labs' services are also suitable for traditional financial firms and government agencies investigating complex crypto-related crimes, including fraud, hacking, and terrorist financing. Esteban Castao, co-founder and CEO of TRM Labs, said that cryptocurrencies are evolving faster than any industry, and organizations need a blockchain intelligence partner that can stay ahead of the changing risk landscape - from ransomware attacks to DeFi exploits.
On May 19, 2022, TRM Labs partnered with Solana and others to launch a community-based scam reporting platform. TRM Labs has partnered with Circle, Solana Foundation, Aave, Hedera, Binance.US, Civic and others to develop the platform, and supported blockchains include Ethereum, Bitcoin, Solana, Polygon, Hedera, BNB Chain and Tron. Crypto users can report illegal activity to the platform’s public forum. Others will then vote up, down, or comment on other information. Information about the same address or entity will be consolidated into a searchable database that allows users to view addresses or items, with the hope that users will be better able to review items before participating in them.
On August 8, 2022, the U.S. Treasury Department announced that it would sanction Tornado Cash, an Ethereum mixing protocol, and blacklist wallet addresses related to the Tornado Cash protocol. In response, the U.S. Treasury Department reasoned that Tornado Cash has been used for more than $7 billion worth of virtual currency laundering since its inception, and it is time to take action against this crime-facilitating currency mixing protocol. As soon as this news came out, many DeFi projects were worried that they would be implicated unknowingly, and took relevant actions in response to the news (for example, the decentralized derivatives exchange dYdX quickly cut off all kinds of encryption with Tornado Cash. address, etc.). And how do these exchanges obtain addresses related to sanctions? Actually through TRM Labs.
In order to obtain on-chain details of sanctioned addresses, the DeFi platform must integrate with TRM Labs' application program interface "TRM Wallet Screening API", which is allowed to query sanctioned addresses and transaction data. In addition, in order to have a clearer understanding of why an address is being sanctioned, the protocol can be set up to retrieve the required information through the API. At the same time, the risk level of sanctioned addresses is also detailed.
proxy

Proxy is a web3 identity wallet designed to be used in blockchain-based products as well as real-life use cases such as unlocking locked doors using Bluetooth technology. Proxy was founded in 2016 by Denis Mars and Simon Ratner. The original intention of Proxy is to hope that people have better interaction with the environment and smart devices, and Proxy is to eliminate the friction. For example, by unlocking the office door, people only need to use their mobile phone to enter the office building, which can replace the key card. The ultimate goal of Proxy is to allow people to do many things without taking out their phones or opening an app.
When Denis Mars and Simon Ratner experimented with IoT devices, they found it was relatively inconvenient for every refrigerator and light bulb to expect users to download an app, set up a profile, enter a password, and then click a button to control an action. At that time, they had the idea of starting a business. They hoped to send encrypted one-time tokens based on blockchain technology, allowing smart devices to recognize everyone and respond (such as opening doors, etc.) through mobile phones. These instructions will involve some private data, and the blockchain technology can well protect private data and prevent the serial modification of one-time tokens (for example, hackers invade the door through technology, etc.). Denis Mars said Proxy was designed to turn a user's phone into a master key, and the door is a mandatory feature that solves all difficult problems -- from security to reliability, from experience to privacy.
Most offices already have employee card based key to open the office door, however many times employees forget their employee card causing a lot of inconvenience. Proxy only needs to integrate with the office's existing access control system, replacing employee cards with an authorized application. The employee can then walk up to a door with a phone within about 6 feet of the sensor, and the door will open. At the same time, the company can also know who has entered and exited the door of the office, and there is no need to set up a punch card system.
Proxy is also perfecting its functionality. Examples include automatically booking a meeting room when a user walks into a meeting room, logging a user into a teleconferencing system when a user approaches a screen, and personalizing a workstation when a user arrives. Proxy also wants to simplify things like check-in for hotel guests, for example. In short, Proxy wants to simplify and intelligentize the way people live, especially office-related activities.
After a demo at Y Combinator at the time, Proxy was contacted by thousands of companies, from hotel chains to conglomerates to theme parks. Many of these companies said they were looking for an alternative for their hardware facilities, punch card systems, etc., and Proxy became the alternative they were looking for. Compared to traditional competitors such as Openpath, which only deal with the gate part, Proxy wants to build a device-wide identity system. Proxy is also partnering with WeWork, hoping to install the system at its headquarters.
Axoni

Axoni is an American technology company specializing in the development of blockchain software for financial institutions. Axoni provides services for blockchain-related technologies to trading firms, infrastructure providers and technology companies in the United States, Europe and Asia. Axoni launches and operates Veris, a distributed ledger system used by large financial companies.
Axoni was founded in 2013 to build and deploy institutional blockchains and distributed ledger technology similar to the technology that powers Bitcoin, known as the Axcore blockchain, which is considered a precursor to the Ethereum blockchain Customized version. It becomes the underlying framework for Axoni's distributed ledger infrastructure.
As of 2020, Axoni's technology and partnerships with other platforms involved in major capital markets projects have processed at least $10 trillion in contracts. For example, its project with the Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation (DTCC) led to the development of the Trade Information Warehouse (TIW), which handles $9.9 trillion worth of clearing and bilateral derivatives . The system is considered a multi-vendor approach and was developed with other tech companies such as R3 and IBM.
Axoni is also a partner of the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), one of the largest equity derivatives clearing organizations in the world. The platform has helped BATS, Cboe, Nasdaq, and the New York Stock Exchange, among others, process $7.52 billion in contracts in one year.
In 2020, Axoni launched Veris, a distributed ledger network that manages equity swap transactions. The system is designed to match and reconcile post-trade data for equity swaps. Companies using the network include BlackRock Inc., Goldman Sachs Group Inc. and Citigroup, Inc. The infrastructure acts as an equity swap platform where participating institutions can maintain ongoing reconciliation of equity swaps until maturity. Transactions synchronize transactions throughout their lifecycle, with participants able to communicate changes in real-time. Its first recorded swap deal involved Citi and Goldman Sachs. It is also based on Axcore technology, adding to an enterprise software suite that provides large-scale data management, automation and development toolkits.